哈佛研究员发现了6个新的基因涉及自闭症, 这些基因在脑子里造成混乱停滞, 以至于不可能适当地形成新的连合.
这个研究发现也帮助解释, 为什么积极强烈的教育规划 (intense education programs) 可以帮助一些自闭症的孩子, 因为某些基因对不消失的经验是有反应, 而这些基因只是被困住而无法发挥功能.
以行为治疗法知名的盖瑞.固斯坦博士( Dr. Gary Goldstein of the Kennedy Krieger Institute in Baltimore, https://www.kennedykrieger.org/kki_staff.jsp?pid=1901)说, “所以你必须在电路那里使劲推动”,他说, “遗传学建议我们的作法是合理的, 当我们不停地用积极强烈的教育规划去推动幼小的自闭儿学习,他们会突然通过学习瓶颈;但是这个研究下的更大讯息是,每个自闭症的现象太不同,以至于不能想象能以一个简单的基因来测试它,反而将自闭症者规化成有广大多样的基因缺陷;波士顿儿童医院的遗传学院长(chief of genetics at Children’s Hospital Boston )克里斯托弗.华席医学博士(Dr. Christopher Walsh)说“几乎每个自闭症的孩子都有他们自己的特殊起因” , 克里斯托弗.华席医学博士专门研究自闭症的源由,并出版在星期五科学学报(Friday’s edition of the journal Science ), 自闭症的现象从脑部的范围下研究很难明白,这个范围包括从温和的Asperger的综合症状,到严重的社交孤立,语言沟通的障碍和重复性的失常行为.
从孪生的家庭到有重复自闭症者的家庭史的广泛研究,基因的确在自闭症中扮演一个大角色.克里斯托弗.华席医学博士说, “但到目前为止,确认是基因起因而有的自闭症案例只有15%(在美国)”, 所以克里斯托弗.华席医学博士的研究团队采取了一项新的策略, 他们转向了中东,一个倾向只有表兄弟/姊妹能结婚的的大家庭世界,以能增加可能性,来发现罕见基因的特征。 他们从乔丹、沙特阿拉伯、科威特、阿曼、巴基斯坦、卡塔尔、土耳其和阿拉伯联合酋长国(Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Turkey and the United Arab Emirates),吸收了88个以表兄弟婚姻且有高机率的自闭症家庭,华席医学博士的研究团队比较了家庭成员中的DNA, 查寻什么是隐性变化(recessive mutations),例如健康正常的父母体内会有继承的缺陷基因,而孩子的自闭症是因继承来自双方父母的缺陷基因.在某些案例中,研究团队发现追踪隐性规则(recessive rule ),他们发现了一大区域的DNA不见了!这个DNA不见的地区在每个家庭中有不同的变化,但至少有六个基因在自闭症中扮演一个角色.
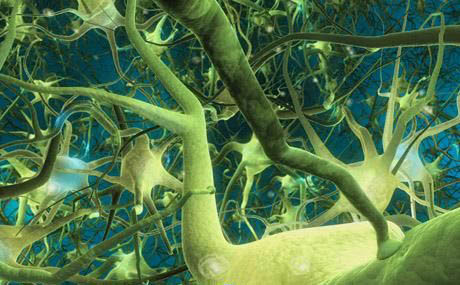
这个发现为什么重要:所有的基因似乎都是一个学习基础网络中的一部分,也就是脑细胞中的神经元借着彼此之间的连接, 称为突触(synapses ),来反应新的经验.在自闭症现象发生的头两年, 突触会迅速地形成并且成熟,而且有多余的部分在后面“被修剪”( pruned ); 换句话说,婴孩的脑子是由他的第一经验被逐渐地塑造,以便使脑能有结构地进行学习和其它最新生活的功能.
By Associated Press – Texarkana Gazette 7/12/2008
H[NextPage]arvard researchers have discovered half a dozen new genes involved in autism that suggest the disorder strikes in a brain that can’t properly form new connections.
The findings also may help explain why intense education programs do help some autistic children—because certain genes that respond to experience weren’t missing, they were just stuck in the “off” position.
“The circuits are there but you have to give it an extra push,” said Dr. Gary Goldstein of the Kennedy Krieger Institute in Baltimore, which wasn’t involved in the gene hunt but is well-known for its autism behavioral therapy. The genetics suggest that “what we’re doing makes sense when we work with these little kids—and work and work and work—and suddenly get through,” he said. But the study’s bigger message is that autism is too strikingly individual to envision an easy gene test for it. Instead, patients are turning out to have a wide variety, almost a custom set, of gene defects. “Almost every kid with autism has their own particular cause of it,” said Dr. Christopher Walsh, chief of genetics at Children’s Hospital Boston, who led the research published in Friday’s edition of the journal Science. Autism spectrum disorders include a range of poorly understood brain conditions, from the mild Asperger’s syndrome to more severe autism characterized by poor social interaction, impaired communication and repetitious behaviors.
It’s clear that genes play a big role in autism, from studies of twins and familie[NextPage]s with multiple affected children. But so far, the genetic cause is known for only about 15 percent of autism cases, Walsh said. So Walsh’s team took a new tack. They turned to the Middle East, a part of the world with large families and a tendency for cousins to marry, characteristics that increase the odds of finding rare genes. They recruited 88 families with cousin marriages and a high incidence of autism, from Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Turkey and the United Arab Emirates. They compared the DNA of family members to search for what are called recessive mutations — where mom and dad can be healthy carriers of a gene defect but a child who inherits that defect from both parents gets sick. In some of the families, they found large chunks of missing DNA regions that followed that recessive rule. The missing regions varied among families, but they affected at least six genes that play a role in autism. Here’s why this matters: All the genes seem to be part of a network involved in a basic foundation of learning—how neurons respond to new experiences by forming connections between each other, called synapses. In the first year or two of life—when autism symptoms appear—synapses rapidly form and mature, and unnecessary ones are “pruned” back. In other words, a baby’s brain is literally being shaped by its first experiences so that it is structurally able to perform learning and other functions of later life.
免责声明:1.凡本站注明“来源:长沙开音”所载的文章、图片、音频视频文件等资料的版权归本中心所有,请务随意转载,; 2.凡本站转载内容如有涉及侵权,请与站内联系方式联系,我们将第一时间处理。